What is Aeroponics? Aeroponic System Definition
Aeroponics is a soilless method of growing plants. Aeroponic system definition - a growing system in which plant roots are suspended in the air and a nutrient-rich solution is sprayed through the air by an aerosol to allow for rapid uptake and growth of the plant roots. Common types are aeroponic tower gardening.

What is Aeroponics?
Aeroponics is an advanced method of soilless plant cultivation (hydroponics) where plant roots are suspended in air and periodically misted with a fine, nutrient-rich solution. It maximizes oxygen exposure and nutrient absorption.
Aeroponic System Definition
An aeroponic system is a closed-loop environment designed to grow plants by:
-
Suspending Plants:
Plants are held in net pots or supports, allowing roots to dangle freely in a dark, enclosed chamber.
-
Misting Roots:
High-pressure pumps and specialized misting nozzles atomize a nutrient solution into tiny droplets (typically 5-50 microns).
-
Timed Cycles:
Roots are misted for short durations (e.g., a few seconds every few minutes) via a timer, ensuring optimal moisture and oxygen levels.
-
Recirculation:
Excess nutrient solution drains back to a reservoir for reuse, minimizing water and fertilizer waste.
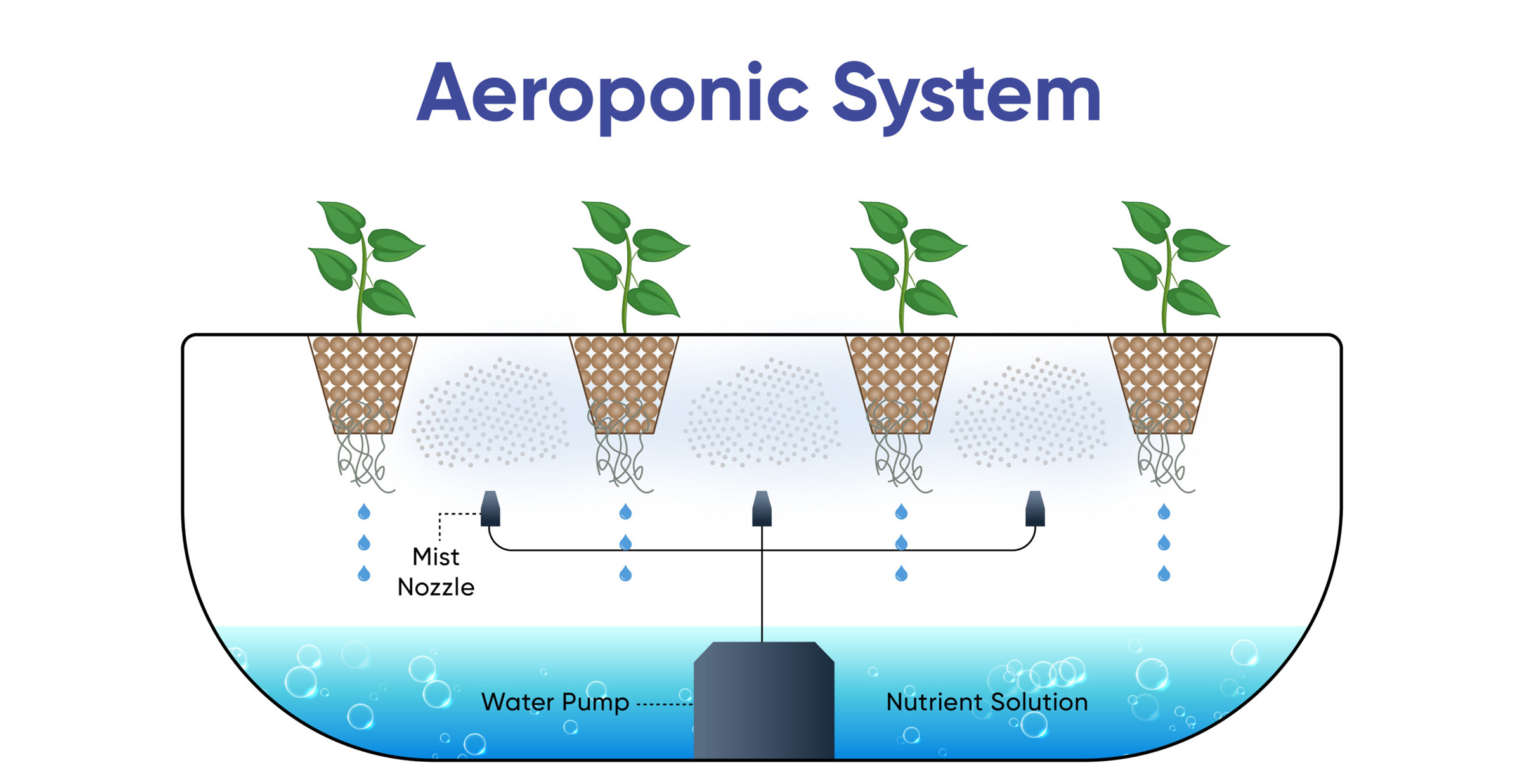
Key Components of an Aeroponic System
-
Reservoir
Holds the nutrient solution.
-
High-Pressure Pump
Generates pressure for atomization.
-
Misting Nozzles
Creates the fine nutrient fog.
-
Enclosed Root Chamber
Dark environment to protect roots and contain mist.
-
Timer/Controller
Precisely controls misting cycles and duration.
-
Plant Support Structure
Holds plants (e.g., foam collars, net pots).
-
Delivery Lines
Transports nutrient solution to nozzles.
-
Drainage
Returns excess solution to the reservoir.
How does an Aeroponic System Work?
An aeroponic system grows plants without soil and with minimal water use by suspending plant roots in air and misting them with a nutrient-rich solution.

Here's how it works step by step
-
Root Suspension
Plants are secured in net pots with stems above and roots dangling in the dark chamber. Roots are exposed to oxygen-rich air.
-
Nutrient Delivery
High-pressure pumps force nutrient solution through misting nozzles, creating an ultra-fine aerosol (5–50 microns). This coats roots with everything they need.
-
Oxygen Advantage
Roots absorb oxygen directly from the air (unlike hydroponics where water limits O₂). This boosts metabolism, accelerating growth.
-
Cyclic Misting
A timer sprays roots intermittently (e.g., 5 sec every 5 min). This prevents dehydration while maximizing oxygen access.
-
Drainage & Recycling
Excess mist drips back into the reservoir, minimizing water waste (uses ~95% less water than soil farming).
Aeroponic Benefits vs. Other Methods
-
Superior Oxygenation
Roots exposed to air absorb maximum oxygen, boosting growth rates significantly (often 30-50% faster than hydroponics).
-
Extreme Water Efficiency
Uses up to 95% less water than soil farming and less than most hydroponics.
-
Nutrient Efficiency
Precise delivery minimizes waste.
-
Reduced Disease Risk
The absence of soil or media reduces pathogens; enclosed chambers protect the roots.
-
Space Efficiency
Vertical stacking is easy (e.g., towers in urban settings).
-
Pesticide-Free
Controlled environments typically do not require pesticides.
-
Year-Round Growth
Independent of soil quality or climate.

Aeroponic Challenges
-
Higher Initial Cost
Requires specialized equipment (pumps, nozzles, controllers).
-
Technical Complexity
Sensitive to pump/controller failures or nozzle clogs.
-
Power Dependency
Requires reliable electricity for pumps and timers.
-
Root Sensitivity
Short interruptions in misting can dry roots quickly.
-
Water Temp Management
Reservoir temperature needs monitoring.
Real-World Applications
NASA pioneered aeroponics for space missions due to its efficiency. Today, it’s used in commercial vertical farms (e.g., AeroFarms) and home systems (like BetiLife™ System, Tower Garden®).
Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in air using a nutrient mist, and an aeroponic system is the precisely controlled technological setup enabling this method by delivering atomized nutrients directly to suspended roots on timed cycles. It prioritizes root zone oxygen and resource efficiency. By maximizing oxygen and nutrients while minimizing water and space, aeroponics outperforms soil/hydroponics in controlled environments, pushing the boundaries of sustainable farming. 🌱💧
If you need to grow vegetable hydroponically indoors or outdoors at home, you can choose BetiLife™ Hydroponic Systems:
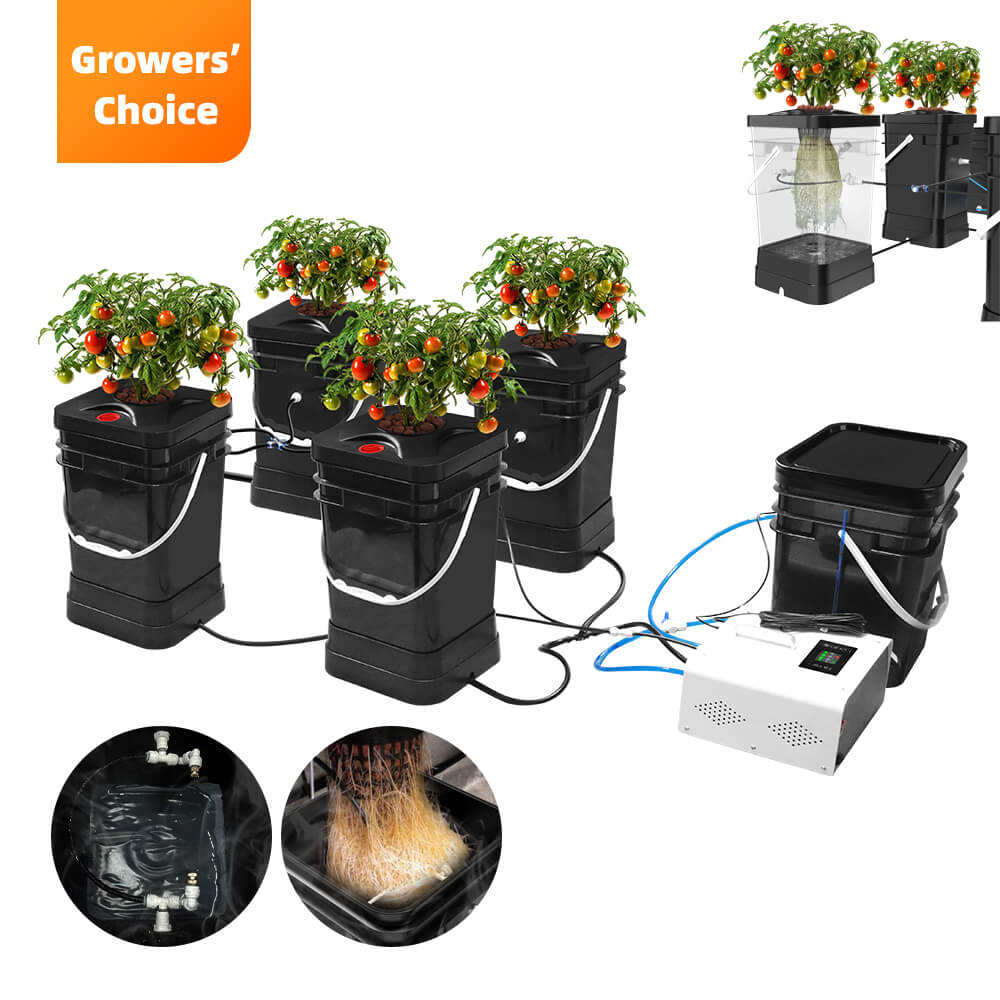

Aeroponic System Kits for Sale
Learn more about hydroponics:
- What Is Hydroponics
- What is a Deep Water Culture
- What is the Nutrient Film Technique
- What is the Ebb and Fow Flood and Drain System
- What is Drip System
- What is the Wick System In Hydroponics
- What Are The Best Flowers For Hydroponics
- How To Grow Hydroponic Tomatoes Indoor
- Can You Do Hydroponic Carrots
- What Are The Best Plants To Grow In Hydroponic Towers
- What Are The Best Hydroponic Lettuce Varieties
- How To Grow Hydroponic Lettuce Indoors At Home
- What Are The Best Strawberries To Grow Hydroponically
- What Are Hydroponic Strawberries






















